Marketplace Implementation: The basics
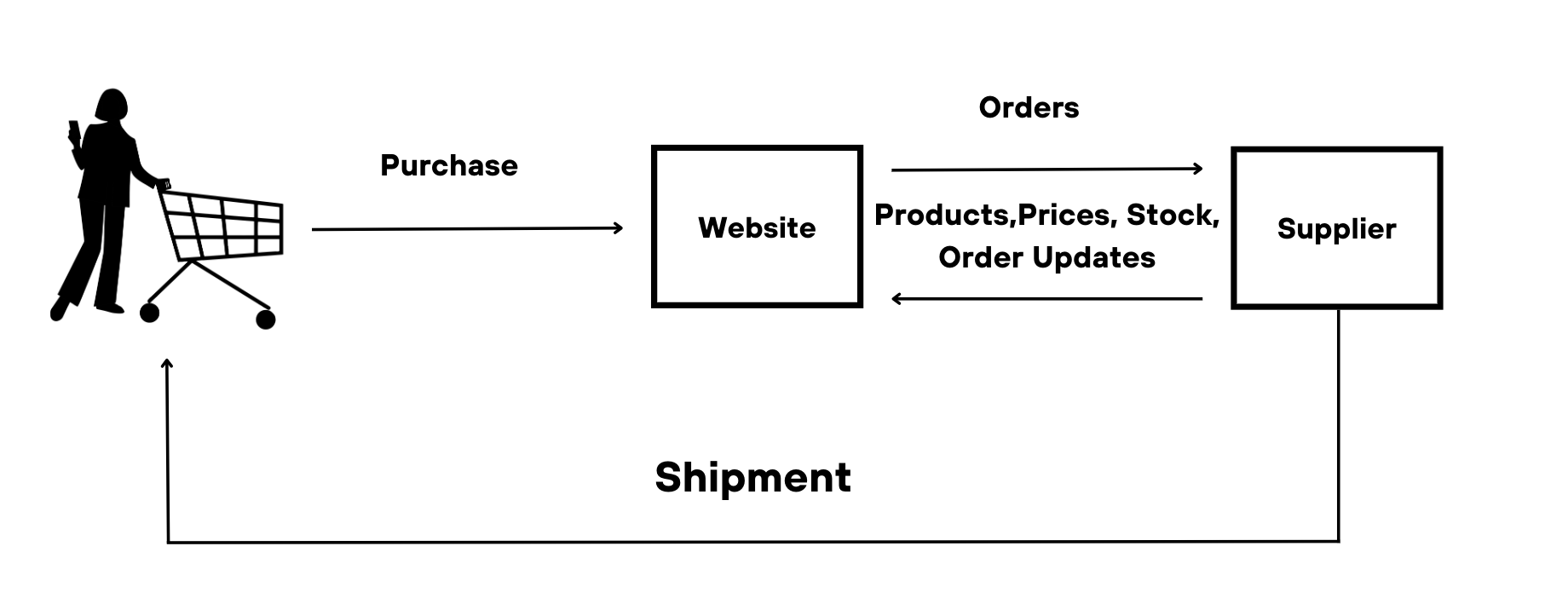
To succeed in a digital marketplace, it is crucial for you as a business to have a clear understanding of its purpose and the different offerings available. In a commission model scenario, let’s consider selling napkins as an example. The marketplace serves as a one-stop shop where customers can purchase napkins along with complementary products like plates or even dining room furniture. To create this marketplace, the operator will onboard third-party vendors to sell their products on the operator’s marketplace, in which the sellers price themselves.
Another offering to consider is if you want to incorporate dropshipping into your marketplace. This will require a dropship model where the seller directly ships the goods to the buyer. For example, if a marketplace typically sells meat but also wants to offer fish or regional and local products, the operator can purchase the goods from a third-party seller and then sell it on their marketplace platform, without physically adding it to their inventory. With a dropship model, the operator is the one who sets the front margin, where they determine the retail price vs the purchase price in order to make a profit. However, some businesses want a hybrid model where the operator would combine their product offerings, as well as commission and dropship models into the same platform. It is important to note that every marketplace is unique, so the requirements and priorities of each business may vary.
Know your business: How to attain a successful marketplace
To achieve a successful marketplace, business stakeholders must have a clear understanding of their chosen marketplace model and their desired objectives. Equally important is the presence of a strong operational team that can effectively oversee the day-to-day operations of the marketplace, ensuring that it runs seamlessly. This team should possess a deep understanding of the relationship between the operator and sellers, enabling them to effectively manage and support both parties in their selling activities. They play a vital role in ensuring that sellers comply with marketplace policies and guidelines and that all operations run smoothly, thereby safeguarding revenue generation.
Having an effective marketplace platform is a crucial part of a successful marketplace as you, the operator, must track and measure the inflow and outflow of products and services. In addition, your system should help monitor the performance of payment processes, and evaluate the marketplace’s product offerings. By implementing an effective marketplace platform, your marketplace can optimise its operations, and ensure a seamless experience for both buyers and sellers.
How do you want to organise your marketplace? The first step is to determine the technology and software you want to use for your marketplace. For example, at e2y we work with Mirakl (as partners) for marketplace implementation. As an operator, one of your key decisions is whether you want to open your marketplace to any seller and their products, so we recommend that you “start slow, and think big”. Deciding on the categories that would expand your line of products and create a one-stop shop is one of the most important decisions to make. For instance, your marketplace could start off by just selling mobile phones, and when it’s more established you can start introducing mobile accessories like phone cases or earphones.
Quality is a key component of running a thriving marketplace – quality products, taxonomy, customer experience and shipping logistics. What happens if a customer receives a damaged phone case? There needs to be a thorough after-sale system that ensures the customer will receive a refund or a replacement phone case. But first, check the quality of this specific seller’s phone case. Are they up to standard? Are there other unhappy customers? Are their delivery methods satisfactory? Are they packaging and delivering on time? The after-care service after such an action is extremely important, as a happy customer, is a loyal customer.
Start slow, and think big
What are the most important topics to cover?
Seller Onboarding and KYC
Seller onboarding is a critical process to ensure a successful marketplace, and using relevant tools can greatly enhance its efficiency. When bringing a third party into your marketplace, it is essential to have a predefined small selection of key partners at the start and to verify their legitimacy as a company. This is to maintain a reputation for happy customers and build a trustworthy business environment. To automate this process and conduct company checks, selecting the right technology and a reliable payment processor is crucial.
When determining whether a seller is financially viable, you need to assess all factors like their financial stability, possessions of a trading licence and compliance with essential requirements like PSC (Persons of Significant Control), KYB (Know Your Business), and KYC (Know Your Customer). You also need to ensure that these factors comply with country-specific regulations, as they vary from country to country.
In marketplace implementation, KYC (Know Your Customer) plays a crucial role in ensuring compliance with regulations, minimising risks, and establishing trust between buyers and sellers. The KYC process begins with the verification of a seller or buyer’s identity, which involves collecting and validating their personal information, like their name, address and ID. This step helps confirm that all users are genuine, and assists in preventing issues like identity fraud or unauthorised access to your marketplace. You should also conduct a background check in order to assess the history and reputation of individuals, or businesses wishing to partake in your marketplace.
To streamline the KYC process, employing advanced technology is highly recommended. Implementing an automated tool for KYC can significantly improve the efficiency and accuracy of your seller onboarding process. Through utilising advanced technology, such as AI, your automated KYC tool can swiftly process large amounts of data to verify customer information. It can also enhance your marketplace’s security measures, helping protect both the marketplace and its users.
Payout
In a marketplace, paying the seller on time is also a key factor in driving a successful seller experience. A pay-out system is a process designed to distribute funds or payments to sellers or vendors for their products, or services sold through the marketplace platform. The system ensures timely and accurate payments, providing sellers with the compensation they are owed, and maintaining a transparent and efficient payout. To optimise your pay-out system and align it with your billing cycle, the marketplace operator has to verify the sellers’ eligibility to sell their products, which is mentioned previously in selling onboarding. Sellers then create product listings, and the marketplace operator verifies product details, images, and attributes to ensure accuracy.
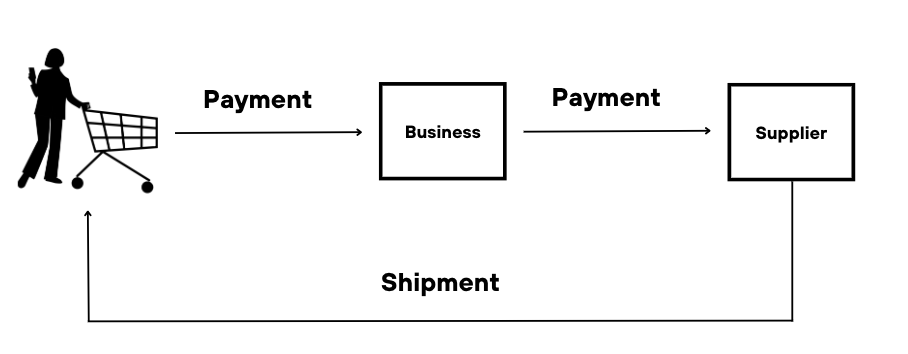
For instance, a customer browses your website, adds items to their cart and then places an order. After approval, the order is sent to your marketplace operator who then accepts it and instructs the seller to ship the product(s), with the funds typically being held in an escrow account until the end of the billing cycle. Once the product(s) has been shipped, the customer will receive the product(s) and validate its condition. Once validated, the seller will receive the money they are owed, minus any commissions or fees (depending on your marketplace structure). The payout to the seller depends on the billing cycle you’ve chosen, for example, every week. With an optimised payout system, both your sellers and customers will be satisfied, ensuring a smooth and happy experience for all.
Pay-in and payment processes
The pay-in process is a step where a customer transfers funds to the marketplace platform, completing the transaction and allowing them to purchase products or services within the marketplace. For a case in point, imagine a customer browsing your marketplace to find the items they need. When ordering multiple items from different sellers, the customer will want the convenience of paying for all their items at once, instead of having to enter their payment details each time. The payment is held somewhere temporarily until the sellers accept their order, a process called capturing the payment. This guarantees that money is set aside until the payment process is completed, which is then used for the payout to the respective sellers.
To facilitate a competent payment process, relevant tools and technology are required to drive this pay-in system by using multi-capture and partial-capture. Multi-capture payment is a feature that temporarily holds the total payment amount for an order with multiple items, as mentioned previously, until all sellers confirm the availability of their products. Partial capture payment allows the platform to capture only a portion of the payment for an order with multiple items, which can then be refunded or void if the items are unavailable or cancelled. For an efficient payment process, the use of a PSP (payment service provider) can automate the process. They also manage the escrow account. At e2y, as experts in payment connectors, we build the connections between a marketplace and a payment system/provider. This will ensure a well-functioning and automated pay-in system that benefits both your customers and sellers.
Another factor to consider is what financial models you want to implement in your marketplace. In Mirakl, there are five models available to choose from:
- In the “Pay on Acceptance” model, when an order is placed in the marketplace, the customer doesn’t pay immediately. Instead, the payment is deducted from the customer’s account after they’ve received their order. This ensures that the customer only pays for what they have received and accepted, increasing customer confidence and satisfaction.
- The “Pay on Shipment” model is where a customer places an order they don’t pay for immediately. Unlike the Pay on Acceptance model, the payment is deducted from the customer’s account after the seller confirms that the items have been shipped. This reduces the risk of fraudulent sellers or delayed shipments, as the payment can only be deducted after the order has been shipped.
- Now, the “Pay on Delivery” model is a little different, as the customer only pays for their order when it’s delivered to them. So, instead of making an upfront payment online, the payment is made only when the order is delivered to their door or collected from a pickup location. This allows the customer to inspect their order before paying, making sure that they are satisfied with their product(s).
- With the “Pay on Due Date” model, the customer makes the payment for their order at a later date. It could even be after the customer has received their order. The payment will be due on a specific date in the future, which is typically agreed upon during the purchase process. This allows the customer to have some time to use or inspect their order, similar to getting an invoice and paying it at a later (specified) date.
- With typical transactions, the customer will need to confirm their payment before the seller receives any money. However, in the “No Customer Payment Confirmation” model, the customer doesn’t need to manually confirm their payment for the order as it is automatically assumed that the payment has been made. So, instead of inputting their account details and then clicking “Pay Now”, in this model, the transaction is made without the customer needing to click any more buttons. This model is typically used in B2B marketplaces, such as SaaS services or wholesale marketplaces.
Taxonomy
Taxonomy has a huge impact on the decision of what will be sold on your marketplace. When defining your product offerings, your marketplace operator will need to consider the attributes of the products, including their brand and specifications. To illustrate, if your marketplace primarily sells phones, you will need to specify their attributes such as price, compatibility with accessories and technological integrations, like Bluetooth. Now, although you need to focus on key product features, as mentioned before, collaborating with your sellers will help you define the attributes that are most important to them and their customers. So, if you have a seller offering phone cases, they may focus on the material of the phone case, its waterproof capabilities, its shock resistance etc., which can be popular selling points for their products.
To avoid unnecessary complexities, your marketplace should maintain a high-level structure in its taxonomy, with a maximum of four levels. With the previous example of selling phones in mind, the four levels could include categories like electronics, phone accessories, mobile devices and specific phone models (Apple or Android etc.). This simplified approach makes it easier for your customers to navigate your marketplace and locate products resourcefully. In addition, while your marketplace sticks to the four primary levels, your sellers can add additional “sub levels” to provide more specific product information. Indexing and taxonomy management are vital in organising and categories products within a marketplace, and by executing them proficiently, you can enhance your customer’s shopping experience.
Taxonomy also plays a crucial role in shaping the shipping methods and delivery options available for your sellers and customers. A good way to ensure a seamless user experience for all is by outlining the delivery options into three options: standard, express, and next day. By defining these three options and sharing them with your sellers, your marketplace will avoid having a multitude of shipping options, which can confuse a customer.
How can e2y help you with your marketplace implementation?
Understanding the concept of a marketplace is crucial, just like running any business, and defining key points and architectural elements is essential, especially when considering your customer experience. As an expert team and proud partners of Mirakl, we at e2y are dedicated to delivering high-quality solutions to ensure for a successful marketplace and a real one-stop-shop experience. With our skilled team, comprised of testers, developers, BAs and product owners, we conduct discovery workshops to ensure a thorough understanding of your project’s requirements and the unique aspects of your marketplace.
We highly value collaboration throughout this process, engaging with various stakeholders, such as BAs, and product owners, to provide optimal solutions for our clients. To foster this collaboration we use Atlassian tools like Jira, which allows us to document the implementation process, including to-do lists, date stamps etc., and ensure that all members of the team, including stakeholders, are on the same page. With this in mind, we also implement strategic questioning, involving the whole company, to ensure that the right personnel are engaged in their appropriate aspect. For example, project managers for catalogues or content managers for marketing content. Aside from collaboration, we make sure to prioritise seller elements, focusing on seller onboarding, product revisions and integration needs, utilising automated connectors like Stripe to streamline the process.
Conclusion
With our expertise and experience, we at e2y can help optimise your marketplace, improving your customer experience and fostering positive relationships between sellers and operators. If you’re ready to take your business to the next step, please contact our expert sales team.
Image by Freepik



